AJNR Case Collection
Section Editors:
Anvita Pauranik, MD, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada
Michael Travis Caton, MD, Mount Sinai South Nassau, New York
Simona Gaudino, MD, Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Italy
Matthew S. Parsons, MD, Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Missouri
Anat Yahav-Dovrat, MD, University of Toronto, Canada
April 7, 2025
Final Diagnosis: Isolated Extranodal Rosai Dorfman Disease of the Skull Base
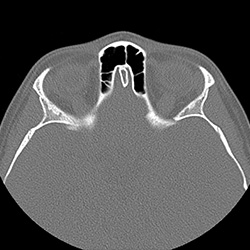


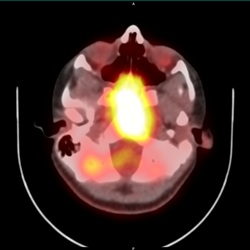
Imaging Findings:
- Paranasal Sinus CT-Axial Bone Window: Paranasal Sinus CT demonstrates a posterior nasopharyngeal mass with extension toward the skull base and clivus with evidence of bone erosion (circles). This mass lesion extends through the sphenoethmoid recess (red arrow) into the ethmoid sinus and the choana (blue arrow) into the right posterior nasal cavity.
- Axial T2-weighted MRI with Fat Suppression: T2-weighted MRI demonstrates a predominantly isointense to gray matter extensive mass lesion involving the roof of the nasopharynx and central skull base. Also, there were hypointense areas in the lesion (blue arrows).
- Axial T1-Weighted Postcontrast MRI: Postcontrast MRI demonstrates a contrast enhancing extensive mass lesion involving the roof of the nasopharynx and central skull base (blue arrows).
- Axial PET-CT of Head: PET-CT demonstrates a large, hypermetabolic nasopharyngeal-central skull base mass (blue arrows) with no other hypermetabolic lesions consistent with isolated Rosai-Dorfman's disease. There is symmetric tonsillar activity (white arrows), which is typically seen in the setting of benign lymphoid hyperplasia.











