This article requires a subscription to view the full text. If you have a subscription you may use the login form below to view the article. Access to this article can also be purchased.
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Intracranial aneurysms (IAs) are the major cause of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stent-assisted coiling, especially with the Neuroform Atlas stent (NAS), has proved more effective than coiling alone for treating these aneurysms.
PURPOSE: To perform a systematic review and meta-analysis to investigate the efficacy and safety of the NAS in treating IAs.
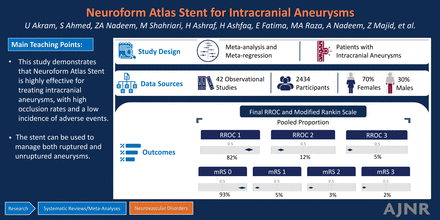
DATA SOURCES: A comprehensive literature search was conducted on PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and clinicaltrials.gov from inception until June 2024.
STUDY SELECTION: We included studies on ruptured and unruptured IAs treated with the NAS, covering experimental, observational, and case series across all age groups. The aneurysm occlusion rate was assessed by using the Raymond-Roy classification (RROC). The mRS and adverse events related to stent use were also recorded.
DATA ANALYSIS: The statistical analysis was conducted on R Version 4.3.2 by using the packages “meta” and “metasens.” We reported our results as proportions with their corresponding CIs. Meta-regression, leave-one-out, and sensitivity analyses were conducted to confirm the robustness of our results.
DATA SYNTHESIS: A total of 42 studies including 2434 participants with a mean age of 51 to 73 years were included. Among angiographic outcomes, the final RROC 1/RROC 2 was achieved in 95% of the patients, final RROC 1 in 82%, RROC 2 in 12%, and RROC 3 in 5% of the patients. Additionally, 93% of the patients showed mRS grade 0, 5% showed mRS grade 1, 3% showed mRS grade 2, 2% showed mRS grade 3, 0% showed mRS grade 4, 0% showed mRS grade 5, and 1% showed mRS grade 6. All adverse events had a ≤5% rate.
LIMITATIONS: Due to limited cause-specific data, we were unable to analyze mortality specific to the stent placement and complications. Despite the large number of studies included, comparative studies were still observed to be scarce.
CONCLUSIONS: Although the generalizability of our findings is limited, this study demonstrates that the NAS is highly effective for treating IAs, with high occlusion rates and a low incidence of adverse events. The stent’s performance, supported by comprehensive analysis, highlights its safety and efficacy in managing both ruptured and unruptured aneurysms.
ABBREVIATIONS:
- EVT
- endovascular therapy
- GLMM
- generalized linear mixed models
- NAS
- Neuroform Atlas stent
- NHLBI
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
- PFT
- Freeman-Tukey double arcsine transformation
- PRISMA
- Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- RROC
- Raymond-Roy classification
- SAC
- stent-assisted coiling
Footnotes
Disclosure forms provided by the authors are available with the full text and PDF of this article at www.ajnr.org.
- © 2025 by American Journal of Neuroradiology