This article requires a subscription to view the full text. If you have a subscription you may use the login form below to view the article. Access to this article can also be purchased.
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
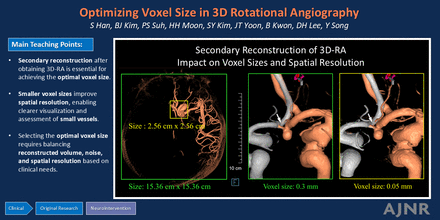
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: 3D rotational angiography (3DRA) is a crucial diagnostic tool for assessing neurovascular diseases. Despite its superior spatial resolution, challenges arise in visualizing minute vasculatures. This study investigates the impact of voxel size on the spatial resolution and noise of cerebral 3DRA.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: 3DRA data from January 2022 to May 2022 were retrospectively analyzed, including a total of 10 patients with 50 small vessels (<1.0 mm in diameter) analyzed (5 vessels per patient). Using the Artis Q biplane angiography machine, 3DRA data sets were acquired and reconstructed at various voxel sizes ranging from 0.05 mm to 0.30 mm. Quantitative assessment included measurement of vessel visibility (maximum grayscale intensity within the vessel), vessel sharpness (slope of grayscale intensity calculated between 20% and 80% of maximum intensity), and background noise (standard deviation within a nonvascular region). Qualitative assessments—sharpness, noise, and overall image quality—were evaluated by 3 neuroradiologists.
RESULTS: A total of 50 vessels were analyzed quantitatively. Both the maximum intensity and slope of grayscale intensity at vessel walls decreased with increasing voxel size. There was a significant 2.94% increase in vessel intensity for every 0.05 mm decrease in voxel size (P < .001). Background noise significantly decreased as the voxel size increased (P < .001). Qualitatively, as the voxel size decreased, the sharpness of the image improved, and the amount of noise decreased. The overall image quality generally improved with decreasing voxel size. A good interrater agreement was observed among the neuroradiologists (κ = 0.601).
CONCLUSIONS: Voxel size significantly influences 3DRA image quality. Smaller voxel sizes enhance spatial resolution and overall image clarity despite increased noise and reduced field of view. Strategic application of smaller voxel sizes is crucial for detailed vascular assessments, such as aneurysm morphology and fine vascular structures.
ABBREVIATIONS:
- 3DRA
- 3D rotational angiography
- EE
- edge-enhanced
- FOV
- field of view
Footnotes
Disclosure forms provided by the authors are available with the full text and PDF of this article at www.ajnr.org.
- © 2025 by American Journal of Neuroradiology