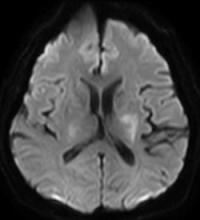
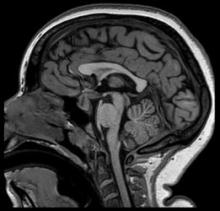
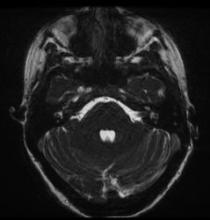
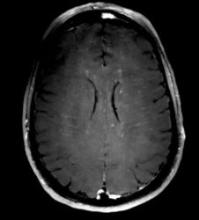
A 79-year-old woman presents with acute onset right-sided hemiplegia, gaze deviation, and receptive and expressive aphasia.
Case of the Week Archive
Section Editors: Matylda Machnowska1 and Anvita Pauranik2
1University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
2University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada
A 52-year-old man presents with headache and left-sided ptosis, miosis, and facial anaesthesia (Horner syndrome) after skiing and coughing.
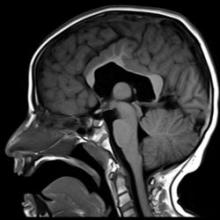
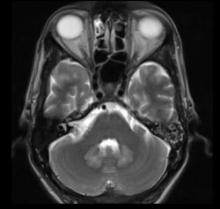
A 7-year-old boy presents with history of intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder.
A 42-year-old man with chronic kidney disease and cervical tubercular lymphadenopathy presents with ataxia and slurring of speech. The patient gives a history of intake of antitubercular therapy including isoniazid, rifampicin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide for 2 months. On neurologic examination, the patient has an ataxic gait with dysarthria.
A 59-year-old man with no known medical illness presents 3.5 hours post acute onset of right-sided body weakness and numbness. MRI shows acute infarct of the left basal ganglia (> 3 contiguous slices), with evidence of DWI and FLAIR mismatch. The NIHSS score is 8 at presentation, but fluctuates to 11. Intravenous thrombolysis with 0.25 mg/kg tenecteplase is administered.
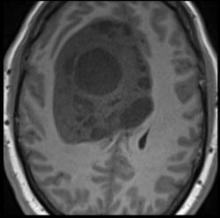
A 30-year-old man with no past medical history presents with bilateral optic disc swelling noted during an outpatient ophthalmology appointment.
A 63-year-old woman with rheumatoid arthritis comes to the ED with a 2-week history of gait disturbance. On physical examination, right hemiparesis is detected, with no other neurologic deficit.
A 14-year-old adolescent girl presents with headache, weight loss, polyuria, and polydipsia. On admission, laboratory workup demonstrates panhypopituitarism.
A young female patient presents with bilateral hearing loss and tinnitus for several weeks. The patient was seen at an urgent care facility with rash and sore throat at symptom onset.
A 48-year-old woman presents with fever for 10 days followed by acute-onset confusion, tetraparesis, and urinary retention. Lumbar puncture shows aseptic lymphocytic meningitis.