This article requires a subscription to view the full text. If you have a subscription you may use the login form below to view the article. Access to this article can also be purchased.
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
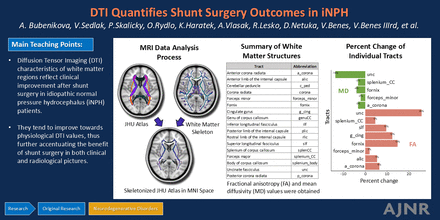
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: White matter changes assessed by DTI typically reflect tract functionality. This study aimed to investigate DTI parameter alterations in important regions pre- and postshunt implantation in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH), alongside assessing the relationship between DTI parameters and clinical improvement.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Patients with probable iNPH underwent prospective preoperative MRI and comprehensive clinical work-up between 2017–2022. Patients with clinical symptoms of iNPH, positive result on a lumbar infusion test, and/or gait improvement after 120-hour lumbar drainage were diagnosed with iNPH and underwent shunt-placement surgery. Fractional anisotropy and mean diffusivity values for individual regions of interest were extracted from preoperative and postoperative MRI. These values were correlated with the clinical picture of individual patients.
RESULTS: A total of 32 patients (73.59 ± 4.59 years) with definite iNPH were analyzed. Preoperative DTI characteristics of internal capsule and corona radiata correlated with the 1-year improvement in the Dutch Gait Scale postoperatively (all P < .036). Cognitive domain improvement after surgery in memory and psychomotor speed correlated with preoperative DTI values of cingulate gyrus (P = .050), uncinate fasciculus (P = .029), superior longitudinal fasciculus (P = .020), or corpus callosum (P < .045).
CONCLUSIONS: DTI characteristics of white matter regions reflect clinical improvement after shunt surgery in patients with iNPH. They tend to improve toward physiologic DTI values, thus further accentuating the benefit of shunt surgery in both clinical and radiologic pictures.
ABBREVIATIONS:
- AVLT
- Auditory Verbal Learning Test
- FA
- fractional anisotropy
- GDS
- Geriatric Depression Scale
- iNPH
- idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus
- LIT
- lumbar infusion test
- MD
- mean diffusivity
- ROCFT
- Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test
- TBSS
- tract-based spatial statistics
- TMT
- Trail-Making Test
Footnotes
Adéla Bubeníková and Vojtěch Sedlák contributed equally to this work.
This work was supported by the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic number NU23-04-00551.
Disclosure forms provided by the authors are available with the full text and PDF of this article at www.ajnr.org.
- © 2025 by American Journal of Neuroradiology