This article requires a subscription to view the full text. If you have a subscription you may use the login form below to view the article. Access to this article can also be purchased.
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
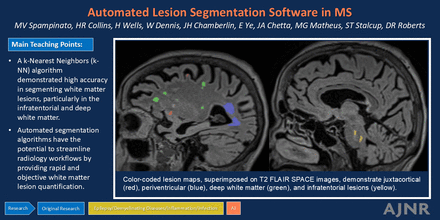
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: MRI is widely used to assess disease burden in MS. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of a commercially available k-nearest neighbors (kNN) network software in quantifying white matter lesion (WML) burden in MS. We compared the software’s WML quantification to expert radiologists’ assessments.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: We retrospectively reviewed brain MRI examinations of adult patients with MS and of adult patients without MS and with a normal brain MRI referred from the neurology clinic. MR images were processed by using an AI-powered, cloud-based kNN software, which generated a DICOM lesion distribution map and a report of WML count and volume in 4 brain regions (periventricular, deep, juxtacortical, and infratentorial white matter). Two blinded radiologists performed semiquantitative assessments of WM lesion load and lesion segmentation accuracy. Additionally, 4 blinded neuroradiologists independently reviewed the data to determine if MRI findings supported an MS diagnosis. The associations between radiologist-rated WML load and kNN model WML volume and count were evaluated with Spearman rank order correlation coefficient (rho) because these variables were not normally distributed. Results were considered significant when P < .05.
RESULTS: The study included 32 patients with MS (35.4 years ±9.1) and 19 patients without MS (33.5 years ±12.1). The kNN software demonstrated 94.1% and 84.3% accuracy in differentiating MS from non-MS subjects based respectively on WML count and WML volume, compared with radiologists’ accuracy of 90.2% to 94.1%. Lesion segmentation was more accurate for the deep WM and infratentorial regions than for the juxtacortical region (both P < .001).
CONCLUSIONS: kNN-derived WML volume and WML count provide valuable quantitative metrics of disease burden in MS. AI-powered postprocessing software may enhance the interpretation of brain MRIs in MS patients.
ABBREVIATIONS:
- 3D DIR
- 3D double-inversion recovery
- AUC
- area under the curve
- EDSS
- Expanded Disability Status Scale
- FN
- false-negative
- FP
- false-positive
- ICC
- intraclass correlation coefficient
- kNN
- k-nearest neighbors
- MP2RAGE
- magnetization prepared 2 rapid acquisition gradient echoes
- ROC
- receiver operating characteristic
- SPACE
- sampling perfection with application-optimized contrasts by using a different flip angle evolution
- WMH
- white matter hyperintensity
- WML
- white matter lesion
- © 2025 by American Journal of Neuroradiology