This article requires a subscription to view the full text. If you have a subscription you may use the login form below to view the article. Access to this article can also be purchased.
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
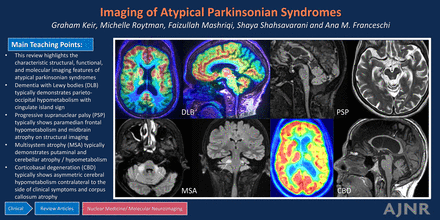
SUMMARY: Atypical parkinsonian syndromes, also known as Parkinson-plus syndromes, are a heterogeneous group of movement disorders, including dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), multisystem atrophy (MSA), and corticobasal degeneration (CBD). This review highlights the characteristic structural, functional, and molecular imaging features of these complex disorders. DLB typically demonstrates parieto-occipital hypometabolism with involvement of the cuneus on FDG-PET, whereas dopaminergic imaging, such as [123I]-FP-CIT SPECT (DaTscan) or fluorodopa (FDOPA)-PET, can be utilized as an adjunct for diagnosis. PSP typically shows midbrain atrophy on structural imaging, whereas FDG-PET may be useful to depict frontal lobe hypometabolism and tau-PET confirms underlying tauopathy. MSA typically demonstrates putaminal or cerebellar atrophy, whereas FDG-PET highlights characteristic nigrostriatal or olivopontocerebellar hypometabolism, respectively. Finally, CBD typically shows asymmetric atrophy in the superior parietal lobules and corpus callosum, whereas FDG and tau-PET demonstrate asymmetric hemispheric and subcortical involvement contralateral to the side of clinical deficits. Additional advanced neuroimaging modalities and techniques described may assist in the diagnostic work-up or are promising areas of emerging research.
ABBREVIATIONS:
- 3D-SSP
- 3D stereotactic surface projection
- AD
- Alzheimer disease
- ASL
- arterial spin-labeling
- APS
- atypical parkinsonian syndrome
- CBD
- corticobasal degeneration
- CBS
- corticobasal syndrome
- CIS
- cingulate island sign
- DaT
- dopamine transporter
- DaTscan
- [123I]-FP-CIT SPECT
- DIP
- drug-induced parkinsonism
- DLB
- dementia with Lewy bodies
- FA
- fractional anisotropy
- FDOPA
- fluorodopa
- MCP
- middle cerebellar peduncle
- MSA
- multisystem atrophy
- MSA-C
- multisystem atrophy–cerebellar
- MSA-P
- multisystem atrophy–parkinsonian
- PA
- posterior atrophy
- PD
- Parkinson disease
- PSP
- progressive supranuclear palsy
- rCBF
- regional cerebral blood flow
- rs-fMRI
- resting-state functional MR imaging
- RSN
- resting-state network
- SCP
- superior cerebellar peduncle
- SMA
- supplementary motor area
- VaP
- vascular parkinsonism
- © 2024 by American Journal of Neuroradiology