This article requires a subscription to view the full text. If you have a subscription you may use the login form below to view the article. Access to this article can also be purchased.
Graphical Abstract
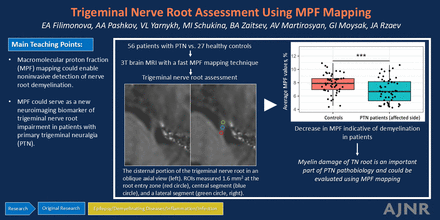
Abstract
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Primary trigeminal neuralgia (PTN) is a prevalent chronic pain disorder. This condition is believed to be associated with demyelination of the trigeminal nerve. Previous studies in this field have focused on diffusion tensor imaging, which has limited sensitivity and specificity to myelin. In the present study, we assessed the trigeminal nerve root via the macromolecular proton fraction (MPF) mapping technique. MPF demonstrated strong correlations with myelin histology in a number of earlier animal studies and is currently viewed as a promising clinical myelin biomarker.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: We performed a prospective case-control study. Fifty-six patients with unilateral PTN and 27 healthy controls were included. All participants were evaluated by using high-resolution brain MR imaging, which included the MPF technique. MPF values from different parts of the trigeminal nerve root, such as the root entry zone (REZ) and central and lateral cisternal segments, were extracted. ANCOVAs were performed. Correlations between MPF values and Sindou grade, duration, and intensity of symptoms were also evaluated in patients with PTN.
RESULTS: A statistically significant decrease in the average MPF of the affected trigeminal nerve root was observed in the PTN group compared with the healthy control group (P < .01, false discovery rate [FDR] corrected). Specifically, reductions in the MPF values of the REZ and central cisternal parts of the affected trigeminal nerve root were found in patients with PTN (P < .01 and P < .05, respectively, FDR corrected). Furthermore, we identified a decrease in the average and REZ MPF values on the affected side compared with the contralateral side in patients with PTN (P < .05 and P < .001, respectively, FDR corrected). A negative correlation between MPF values in the REZ and Sindou grade was revealed (R = −0.35, adjusted P < .05).
CONCLUSIONS: Our preliminary results suggest that MPF could serve as a new neuroimaging biomarker of trigeminal nerve root impairment in patients with PTN and enable noninvasive detection of nerve root demyelination.
ABBREVIATIONS:
- BPI
- Brief Pain Inventory
- FA
- flip angle
- FDR
- false discovery rate
- IQR
- interquartile range
- MD
- mean between-group differences
- MPF
- macromolecular proton fraction
- MT
- magnetization transfer
- PD
- proton attenuation
- PTN
- primary trigeminal neuralgia
- REZ
- root entry zone
- TN
- trigeminal neuralgia
- © 2025 by American Journal of Neuroradiology