This article requires a subscription to view the full text. If you have a subscription you may use the login form below to view the article. Access to this article can also be purchased.
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
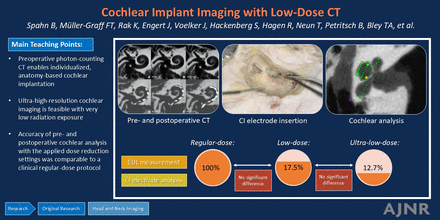
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Anatomically adapted cochlear implantation and efficient postoperative cochlear implant-fitting strategies benefit from reliable and highly detailed imaging techniques. Since image quality in CT is related to the applied radiation dose, this study aimed to evaluate low-dose cochlear imaging with a photon-counting detector by investigating the accuracy of pre- and postoperative cochlear analysis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Photon-counting CT images of 10 temporal bone specimens were acquired with 3 different radiation dose levels (regular dose: 27.1 mGy, low dose: 4.81 mGy, and ultra-low dose: 3.43 mGy) before and after cochlear implant electrode carrier insertion. A clinical scan protocol was used with a tube potential of 120 kV in ultra-high-resolution scan mode (detector collimation 120 × 0.2 mm). The accuracy of cochlear duct length measurements for the organ of Corti and electrode contact determination was investigated for all applied settings by 2 independent otosurgeons.
RESULTS: No substantial differences were ascertained between photon-counting CT scans performed with standard dose and dedicated low-dose imaging regarding the accuracy of neither pre- and postoperative cochlear analysis nor postoperative cochlear implant electrode analysis. Radiation dose reduction of 82.3% (low dose) and 87.3% (ultra-low dose) could be realized compared with the clinical standard protocol.
CONCLUSIONS: Ultra-high-resolution cochlear imaging is feasible with very low radiation exposure when using a first-generation photon-counting CT in combination with dedicated low-dose protocols. The accuracy of pre- and postoperative cochlear analysis with the applied dose reduction settings was comparable with a clinical regular-dose protocol.
ABBREVIATIONS:
- AID
- angular insertion depth
- CDL
- cochlear duct length
- CDLLW
- cochlear duct length of the lateral cochlea wall
- CDLOC
- cochlear duct length of the organ of Corti
- CTDIvol
- volume CT dose index
- DLP
- dose-length product
- EID
- energy-integrating detector
- ICC
- intraclass correlation coefficient
- IL
- insertion length
- LD
- low dose
- PCD
- photon-counting detector
- RD
- regular dose
- SD
- standard deviation
- ULD
- ultra-low dose
- © 2025 by American Journal of Neuroradiology