We thank Paula Alcaide-Leon and Álex Rovira for their interest in our work.1 In a given a time-series model involving a number of parameters, it is reasonable to expect that a determination of the parameters by using very few time points may result in erroneous estimates due to noise in the data. However, if one uses enough time points, the computations are expected to be relatively error-free; the inclusion of too many time points need not result in any better estimates.
Furthermore, if the model describes the data (ie, it is applicable), the variability in the parameter estimates using variable time points should only be random. A systematic variation in estimated parameter with respect to variable time points is indicative of an inadequacy of the model to describe the data.
The generalized tracer kinetic model (GTKM) given by
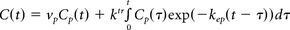 is a 2-compartment model used by the commenting authors.
is a 2-compartment model used by the commenting authors.
To resolve the persistence of uptake, researchers are using a model that assumes unidirectional exchange (ie, from the capillary plasma to the extracellular extravascular space [EES]2⇓–4), which essentially consists of the Patlak model:
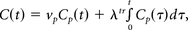 describing a pure contrast uptake voxel.
describing a pure contrast uptake voxel.
The actual situation, however, appears to be best described by the 3-compartment leaky tracer kinetic model (LTKM)5:
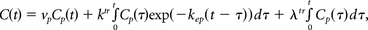 presented in Rathore et al6,7 and Sahoo et al.8
presented in Rathore et al6,7 and Sahoo et al.8
LTKM reduces to GTKM if the leakage space is absent (λtr = 0); and it reduces to the Patlak model in the absence of a permeable space (ktr = 0).
The systematic variability of the tracer kinetic parameters using GTKM and its cessation using LTKM is considered at length in Sahoo et al.5
In short, it not necessary to prolong the observations until the washout phase, and a study of approximately 3 minutes is quite adequate. What is needed is to use the correct model in which the constancy of the parameters is restored to its original state. For further discussion of LTKM, readers may refer to Sahoo et al.5
We used only an in-house-developed code for our computations.
- © 2013 by American Journal of Neuroradiology












