Abstract
Summary: Relapsing polychondritis is a rare inflammatory disorder of cartilage with well-established clinical features and imaging characteristics. Abnormal calcification and erosion of cartilaginous structures are the traditional radiographic findings. As with any disease, aberrancies of the expected clinical presentation may lead to a delayed (or missed) diagnosis. We discuss a rare case of relapsing polychondritis in which the diagnosis was suggested on the basis of CT findings, despite uncharacteristic clinical and radiographic manifestations of the disease.
Relapsing polychondritis is a rare autoimmune disease characterized by recurrent inflammation and eventual destruction of cartilage throughout the body. Frequently affected sites include the external ears, nose, larynx and upper airway, tracheobronchial tree, eyes, and large joints (1). Several radiographic findings can suggest the diagnosis of relapsing polychondritis, including destruction of the nasal cartilage and abnormal calcification of the trachea and lower respiratory tract (2,3). We report a case of a young man whose diagnosis of relapsing polychondritis was suggested by unusual CT manifestations of the disease.
Case Report
A 20-year-old man with a history of asthma and environmental allergies presented to the emergency department of an outside hospital with progressive respiratory distress. During the previous 6 months, he had several upper respiratory and ear infections that were treated with numerous antibiotic courses. His shortness of breath was attributed to his asthma, and he was sent home on a course of oral steroids. The patient noted only mild improvement in symptoms, and he returned to the emergency department twice in the next 2 weeks with similar symptoms. On his third visit, the patient was admitted to the hospital, and at that time, the presumptive diagnosis was multiple food allergies with repeated anaphylaxis. Within 5 days, worsening stridor led to tracheostomy placement.
Initial laboratory studies were significant for a white blood cell count of 19.9, normal rheumatoid factor, and an erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 124. Chest CT showed complete collapse of the left lower lobe, and a neck CT showed no evidence of subglottic stenosis. He was then transferred to our tertiary care hospital for further evaluation and treatment.
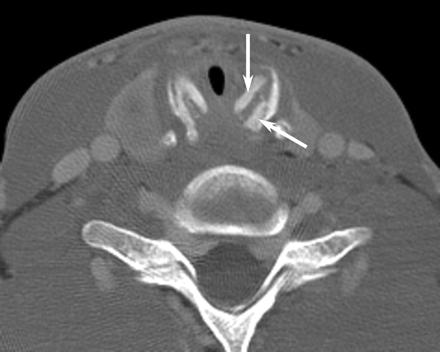
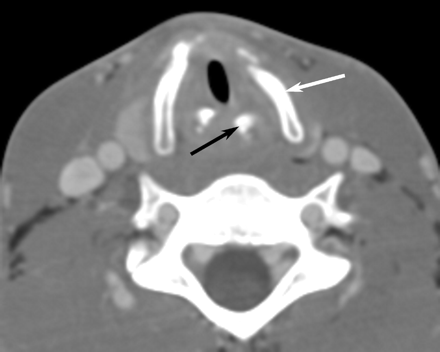
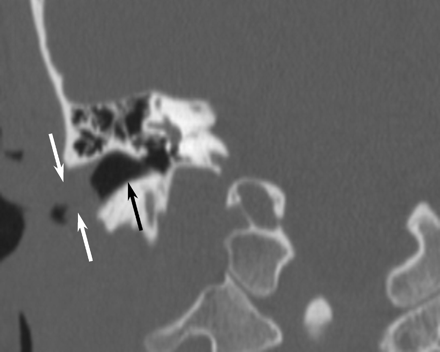
The patient underwent laryngoscopy, which revealed subglottic edema. CT of the neck and chest was repeated with particular attention to the larynx. In the neck, there was marked thickening of the cricoid cartilage with a symmetric “train-track” calcification pattern (Fig 1) and severe subglottic narrowing from edema. The laryngeal cartilages were completely ossified, which is unusual in a 20-year-old patient (Fig 2). In the chest, the findings included occasional discontinuous calcifications of the tracheobronchial tree. Chest CT also confirmed left lower lobe collapse with central bronchial narrowing, as well as patchy air space disease in the right lung. CT of the sinuses was performed to exclude Wegener’s granulomatosis. Although the sinuses and nasal cavity were normal, there was moderate soft-tissue thickening in the cartilaginous portions of both external auditory canals, with complete sparing of the bony portions of the canals (Fig 3).
On the basis of these unusual radiologic findings, the diagnosis of relapsing polychondritis was suggested, and the patient underwent a biopsy of his left ear cartilage. The biopsy revealed acute and chronic inflammation of the perichondrium and cartilage, with patchy necrosis and destruction of the cartilage, as well as mild chronic inflammation. These findings were consistent with the histologic changes of relapsing polychondritis.
The patient received high-dose intravenous steroids while in the hospital and was placed on an oral steroid regimen after discharge. When he was seen 1 month later in the rheumatology clinic, he had new complaints of left eye redness, which was diagnosed as episcleritis and arthralgias of his knees and ankles. A repeat laryngoscopy revealed diffuse boggy edema with obstruction of the subglottic airway, for which laryngeal dilation and local soft-tissue steroid injection were performed. Follow-up CT of the neck and chest showed worsening tracheobronchial stenosis. Despite the addition of methotrexate to his regimen, he continued to do poorly 6 months after diagnosis, with rapid progression of multiple systemic complaints.
Discussion
Although the cause of relapsing polychondritis remains unclear, an immune-mediated mechanism is postulated. Among the supporting evidence is the finding that antibodies to specific collagen types are found in some patients with relapsing polychondritis (4), as well as an increased incidence of autoimmune disorders in patients with this disease (5). Relapsing polychondritis may develop at any age, but most cases are diagnosed in the fourth to fifth decades of life, predominantly among whites, with an equal sex distribution (1).
The most frequent clinical features of relapsing polychondritis are recurrent pain and swelling of the external ear and nose, uveitis, and arthropathy of the peripheral joints. Involvement of the ear results in pinna deformity, and involvement of the nose results in a classic “saddle” deformity of the nasal bridge.
The respiratory tract is involved in approximately half of patients. Clinical symptoms include dyspnea, cough, wheezing, stridor, and dysphonia. Approximately 14% of patients have respiratory symptoms at initial presentation (1), but this subset of patients appears to have a more fulminant course of disease that is less responsive to steroid treatment (6). In general, respiratory involvement portends a worse prognosis because the cause of death is related to respiratory failure in almost half of all reported cases (1). Respiratory distress may occur by 2 mechanisms: collapse of the central airway from destruction and fibrosis of the laryngeal and tracheal cartilages, or peripheral airway narrowing from inflammation and cicatricial fibrosis. Similar pathology in the peripheral bronchi leads to pneumonia, which is a more chronic process but is the other major respiratory cause of death (1).
Many imaging techniques have been used for evaluation and monitoring of patients with relapsing polychondritis. Chest radiography can detect tracheal and main bronchial narrowing (7). Airway fluoroscopy can demonstrate central airway collapse during expiration (8). Radiographic features of the nonerosive arthropathy associated with this disease have also been described (8, 9). Nuclear medicine may play a role in the initial work-up because bone scintigraphy has been shown to be helpful in suggesting the diagnosis in a handful of case reports (10, 11). Laryngotracheal abnormalities are well demonstrated on MR imaging, but there are inherent drawbacks to this technique, including a prolonged examination time, inadequate identification of calcifications, and image degradation due to respiratory motion. It has been suggested that MR imaging be used as a complementary examination to CT in the evaluation of relapsing polychondritis (12).
CT has become the most useful imaging technique because of its superb resolution of cartilaginous and soft-tissue structures, as well as its wide availability and excellent safety profile as a noninvasive means of investigation. It provides a detailed anatomic evaluation of both upper and lower airways. In fact, CT is better than bronchoscopy at early detection of the disease (13). Typical CT findings of relapsing polychondritis include subglottic stenosis, tracheobronchial luminal narrowing (3), densely calcified and thickened tracheal cartilage (2), peripheral bronchial narrowing and bronchiectasis (14), calcifications of the pinnae, and nasal cartilage collapse (15). The most frequent CT manifestations of relapsing polychondritis are increased attenuation and smooth thickening of the airway walls (16).
Tracheobronchial luminal narrowing is not specific to relapsing polychondritis. Other causes that should be considered include tracheopathia osteochondroplastica, trauma, infection, Wegener’s granulomatosis, sarcoidosis, and amyloidosis.
Although our patient had calcification of the trachea and mainstem bronchi, the calcification pattern was spotty rather than continuous, and the typical wall thickening was absent. He had no calcifications in the nose or pinna, and no peripheral bronchial changes were noted, although the central bronchi were sufficiently involved to cause lobar collapse. Our patient also lacked the classic clinical findings of saddle deformity of the nose and attenuated ear pinnae.
The CT findings that allowed the diagnosis of relapsing polychondritis in this patient were inflammation of the cartilaginous portions of the external auditory canal and train-track calcifications of the posterior cricoid cartilage. The advanced calcification of the remaining laryngeal cartilages, as well as the spotty tracheobronchial calcifications, helped to confirm the radiographic diagnosis. Even in the absence of classic radiographic findings, unusual calcifications of cartilaginous structures should suggest the diagnosis of relapsing polychondritis.
Contrast-enhanced axial CT scan with bone reconstruction through the larynx demonstrates unusual “train-track” calcifications (arrows) of the cricoid cartilage.
{/CAPT;;;center;stack;2112n}
Contrast-enhanced axial CT scan through the larynx with soft-tissue reconstruction demonstrates complete ossification of the thyroid (white arrow) and arytenoid (black arrow) cartilages, which is unusual in a 20-year-old patient.
Unenhanced CT scan of the paranasal sinuses in oblique coronal reformat along the external auditory canal shows markedly thickened cartilaginous canal walls (white arrows), whereas the bony canal (black arrow) is spared.
Footnotes
Presented at the ASNR Annual Meeting, May 2004.
References
- Received October 19, 2004.
- Accepted after revision October 28, 2004.
- Copyright © American Society of Neuroradiology