Abstract
Summary: We report a case of a spinal intradural capillary hemangioma. On MR images, a well-circumscribed intradural mass was detected at the T8–T9 level. The signal intensity of the mass relative to the spinal cord was isointense on T1-weighted images, hyperintense on T2-weighted images, and showed homogeneous, strong enhancement on contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images. The mass had both extramedullary and intramedullary components.
Capillary hemangiomas are typically superficial lesions found in the skin or mucosa of the head and neck; intradural locations are rare (1–4). We report a case of an intradural capillary hemangioma in the thoracic spine.
Case Report
A 66-year-old woman initially presented with an 8-month history of lower back pain. A month before admission, she had begun to use a wheelchair owing to weakness of the lower extremities. Preoperative neurologic examination revealed grade 3 paraparesis and sensory abnormality.
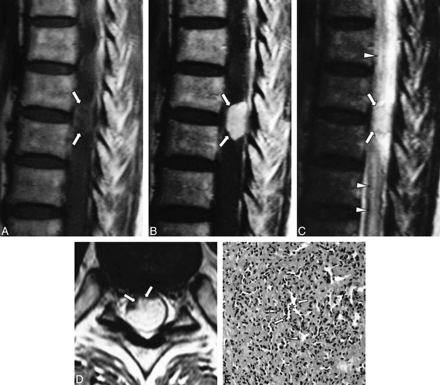
MR studies of the thoracic spine showed a well-defined intradural mass at the T8–T9 level with a diameter of 1.3 cm and a length of 2 cm. The signal intensity of the mass relative to the spinal cord was isointense on T1-weighted images, hyperintense on T2-weighted images (Fig 1A and C), and showed homogeneous, strong enhancement on contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images (Fig 1B and D). The spinal cord was compressed and displaced anteriorly and to the right (Fig 1D), which caused diffuse cord edema from T4 to the level of the conus medullaris (Fig 1C). The mass had an intramedullary component in the posterior aspect of the spinal cord (Fig 1D).
66-year-old woman with lower back pain.
A, T1-weighted (550/12 [TR/TE]) sagittal MR image shows a well-defined, oval mass at the dorsal aspect of the T8–T9 level (arrows). The signal intensity of the mass is isointense with the spinal cord.
B, Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted (550/12) sagittal MR image shows homogenous, intense enhancement of the mass (arrows).
C, On T2-weighted (3600/112) sagittal MR image, the signal intensity is hyperintense relative to the spinal cord (arrows). Note the associated diffuse cord edema (arrowheads).
D, On contrast-enhanced T1-weighted (874/12) axial MR image, the spinal cord is markedly compressed by the posterolaterally located mass (arrows).
E, Low-power photomicrograph shows the tumor to be composed of variably sized but relatively small capillaries (asterisks), pericytes (arrows), and some stromal cells (fibroblasts) (arrowheads) (hematoxylin-eosin, original magnification ×100).
At laminectomy of the T8–T9 vertebrae, a reddish mass was seen upon resection of the dura. The mass, which was easily separated from the dura, had a broad base with the spinal cord, and adhered to it. Removal of the mass was incomplete, owing to significant bleeding that occurred during the operation, and a duraplasty was performed after the mass was removed. The surgeon thought the mass was primarily subpial, as it grew exophytically into the subarachnoid space.
Microscopically, the lesion was composed of capillary-sized blood vessels and a little stroma; there were no foamy stromal cells, as seen in hemangioblastomas (Fig 1E). Factor VIII-related antigen, which is a marker for endothelial cells, was strongly immunoreactive in the lining cells of the capillaries. Smooth muscle actin immunoreactive cells surrounding the capillaries were considered to be pericytes. The diagnosis was capillary hemangioma.
After surgery, the lower extremity weakness and the lower back pain improved markedly, and the patient was able to walk unassisted. A follow-up MR examination 6 months later showed no definite residual tumor, and there was resolution of the previous cord edema.
Discussion
Hemangiomas are common soft-tissue tumors, especially in children (5). They are seen in cutaneous and subcutaneous locations but have rarely been encountered in the neuraxis (1–4, 6–8). Histologically, hemangiomas are divided into capillary and cavernous types, depending on the dominant vessel size at microscopy (4, 5). Capillary hemangiomas are the more common form and consist of capillary-sized vessels lined with flattened endothelium separated by a collagenous stroma. They usually appear in childhood, but some cases are found in adults. Within the neuraxis, cases of capillary hemangiomas in the meninges, cauda equina, epidural, or intramedullary locations are rare (1–4, 6, 9). In the intradural spine, only a few cases of capillary hemangioma of the cauda equina or of a purely intramedullary location have been reported (1–4).
The MR findings in this case are similar to those in previously reported capillary hemangiomas at other sites (5, 6, 9). That is, the signal intensity is isointense with the spinal cord on T1-weighted images, hyperintense relative to the spinal cord on T2-weighted images, and shows homogeneous, strong enhancement on contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images. Because the tumor in this patient was primarily intradural extramedullary, the differential diagnosis with other intradural extramedullary tumors was important. These signal characteristics could help differentiate this type of tumor from meningioma, a much more common intradural extramedullary tumor, as meningiomas display low or isointense signal intensity on T2-weighted images. Because the signal characteristics of the intradural hemangioma are similar to those of intradural extramedullary neurogenic tumors, such as schwannoma, differentiating between the two is difficult.
The anteriorly displaced spinal cord and adhesions of the mass to the posterolateral aspect of the spinal cord were observed during surgery. We speculated that this capillary hemangioma originated from penetrating pial plexus of the posterior spinal artery in the superficial portion of the spinal cord and had grown exophytically into the intradural extramedullary subarachnoid space. Although the natural history of capillary hemangiomas has not been well described, there is a significant risk of bleeding and enlargement, leading to neurologic deterioration. The current treatment of an intradural hemangioma consists of total excision (7).
Acknowledgments
We thank Dae Chul Suh, Choong Gon Choi, and Sung Chul Rhim for their continuous support.
Footnotes
↵1 Address reprint requests to Ho Kyu Lee, MD, Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Asan Medical Center, 388-1 Poongnap-Dong, Songpa-Ku, Seoul, 138-736, South Korea.
- Received August 30, 1999.
- Copyright © American Society of Neuroradiology