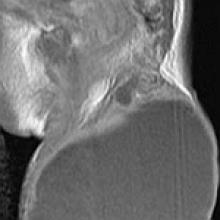
Sacrococcygeal Teratoma
- Sacrococcygeal teratoma is the most common presacral germ cell tumor in children and the most common solid tumor in neonates.
- Most present with a presacral/pelvic mass palpable on rectal exam.
- Majority (70%) are diagnosed in the first few days of life. Few ( <_10 are="are" diagnosed="diagnosed" after="after" _2="_2" years.="years." older="older" the="the" age="age"> the risk of malignancy.
- There are 4 types: I: large external mass with a small presacral component, II: external mass with a large intrapelvic component, III: external mass with pelvic and abdominal component, IV: internal mass with intrapelvic and abdominal location
- Key Diagnostic Features: Depends on the contents (fluid, fat, calcification, soft tissue). Predominantly cystic lesions are benign. Enhancing soft tissue, hemorrhage suggests malignancy. MR is the modality of choice to evaluate for diagnosis, extent and recurrence.
- DDx: Sacral meningocele, dermoid, enteric cyst, lymphatic malformation and neurogenic masses.
- Treatment: Surgical excision.