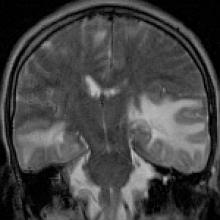
Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy-Related Inflammation
- Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) is characterized by the deposition of amyloid substance within the pial and meningeal vessel walls.
- Usually seen in the elderly normotensive population, it presents as a stroke or with mental status changes, personality changes, and dementia.
- Key Diagnostic Features: CAA is characterized by lobar, fairly large hemorrhages of different ages. In addition, multiple subcm foci of susceptibility suggestive of hemorrhage will be seen on gradient-echo and susceptibility-weighted images. Often, these hemorrhages are present at the gray-white matter junction. Occasionally, associated adjacent edematous change will be seen.
- DDx: Amyloidomas, brain tumor, infection, demyelination
- Rx: Conservative therapy, surgical resection, and immunosuppressive Rx